In Windows operating systems, System Restore and Shadow Copies are used to create restore points that can be used to return your system files and settings to an earlier point in time without affecting your personal files.
- System Restore is enabled by default when you install Windows. It creates restore points automatically every week, and just before significant system events, such as the installation of programs like antivirus, Office, Adobe software, or device drivers.
- Shadow Copies is not enabled by default. You must configure it before you can use it to protect your system or your files from deletion. Shadow Copies creates a copy of a file before any changes are made to it. You can configure Shadow Copies to create preview copies automatically or manually.
If you need to know more about Shadow Copies on Windows, you can read the article “How Volume Shadow Copy Service Works” on the Microsoft Technet website.
How to Delete System Restore and Shadow Copies?
Deleting some other extra files on your system needs to be done carefully. However, you don’t need to worry about deleting system restore points, because they only remove cached restore points that were created when changes were made to your system. System restore points keep only the last restore point.
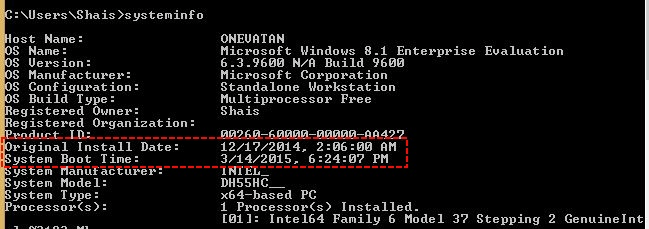
Knowing how much disk space is reserved by restore points, depends on your system’s installation date. If you have been using your system for one year, the caches might be reserved for half of your system drive.
To see the installation date of your Windows, type the “systeminfo” command on the command prompt (cmd.exe). This will show you the entire system information. You can then find out the time of your system’s installation from the screenshot.
To free up a huge amount of space from extra caches, go to System Properties > System Protection tab. Under the protection systems, you will see the enabled ones with the Protection is On label.
To open System Properties, right-click on the My Computer icon on your desktop and select Properties. Then, click on the Change Settings link on the right side of the screen.
Alternatively, you can type Sysdm.cpl on the Run or cmd prompt.
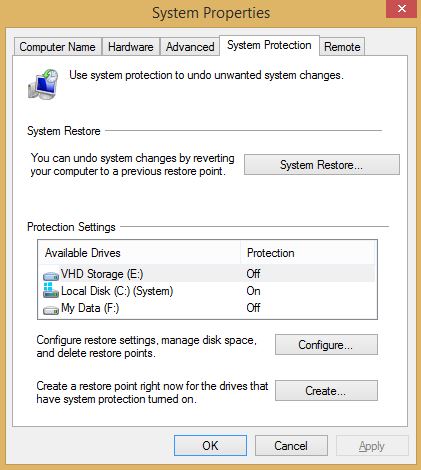
In my system, it’s only enabled for the Windows drive. So let’s try to delete it. To delete system restore and shadow copies, follow these steps:
- Go to My Computer and right-click on the Windows Drive.
- Click Properties.
- On the General tab, click Disk Cleanup.
- It may take a few moments for Disk Cleanup to estimate the amount of space that can be freed up.
- Select the System Restore and Shadow Copies checkbox.
- Click Clean up system files.
Disk Cleanup will then delete the system restore and shadow copies from your computer. For more information, you can read the articles about Disk Cleanup and temporary files. How to delete temporary files in Windows? It is also a good practice to clean up the system.
So, on the Disk Cleanup, click the Clean up system files button. This will open the System Cleanup. On the Disk Cleanup for the drive (C:) page, click the More Options tab. You can see and delete System Restore and Shadow Copies from here. Read the details and click the Clean up button to completely remove and delete system restore and shadow copies.
Now, check your system drive. It freed up my system drive by over 35 GB, and I’m really happy. Do it on your system and get your hard disk free from cached files.
It is the result of my Server.
If you have any questions or problems feel free and ask through the comment.
